Multirate Filtering for Digital Signal Processing: MATLAB® Applications, Chapter 9: Multirate Techniques in Filter Design and Implementation - Exercises
Contents
Exercise 9.1
Design a lowpass FIR filter composed of a cascade
of a factor-of-2 decimator, kernel filter and factor-of-2 interpolator.
The specifications for the overall filter are the following:
- Sampling frequency: F0 = 10000 Hz
- Passband edge frequency Fp = 800 Hz
- Stopband edge frequency Fs = 1000 Hz
- Minimal attenuation in the stopband as = 60 dB
- Peak passband ripple δp = 0.01.
- Decimation and interpolation filters are identical halfband
filters.
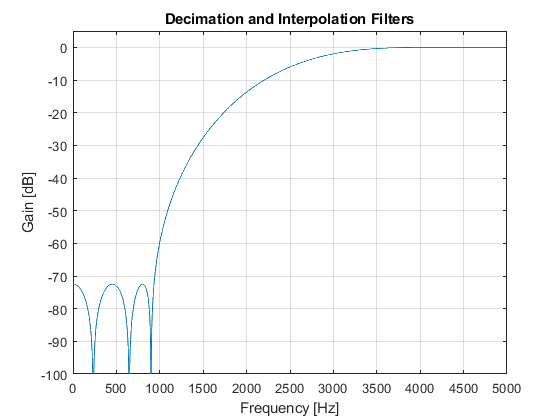
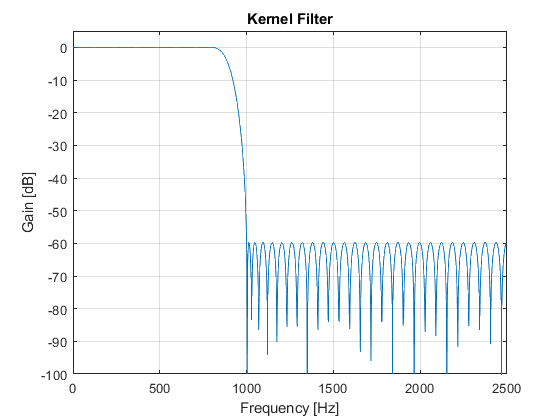
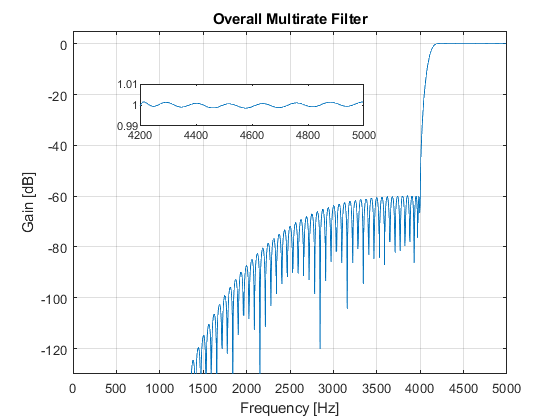
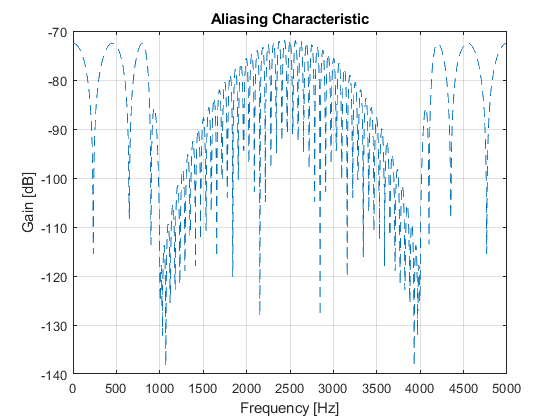
Compute and plot:
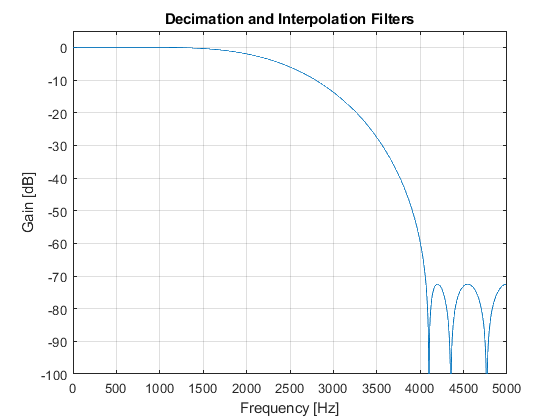
- Magnitude responses of decimation and interpolation filters
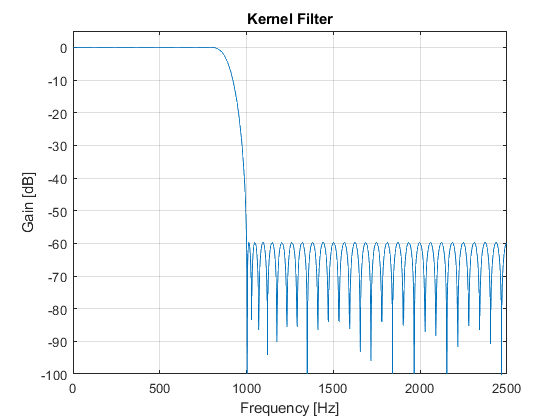
- Magnitude response of the kernel filter
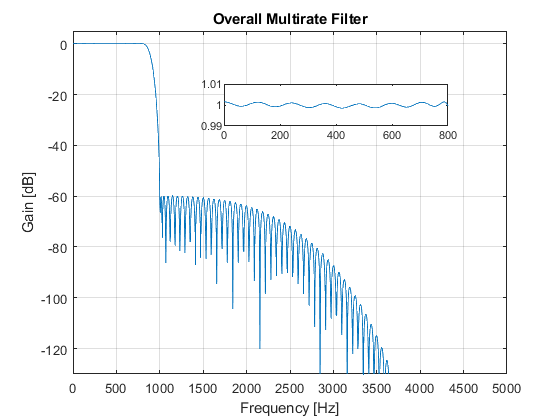
- Magnitude response of the overall multirate filter
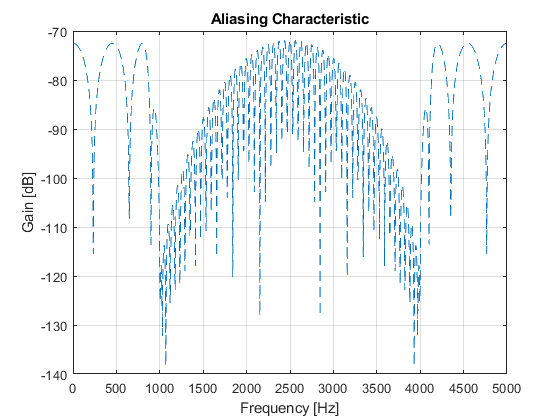
- Aliasing characteristic of the overall filter.
Used functions firgr (DSP System Toolbox), freqz (Signal Processing Toolbox)
close all, clear all F0 = 10000; % Sampling frequency [Hz] Fp = 800; % Passband edge frequency [Hz] Fs = 1000; % Stopband edge frequency [Hz] delta = 0.001; % Peak stopband ripple Nord_k = 82; % Setting the kernel filter order hk = firgr(Nord_k,[0,2*Fp/(F0/2),2*Fs/(F0/2),1],[1,1,0,0]); % Designing the kernel filter hd = firhalfband('minorder',(2*Fs + Fp)/(3*F0/2),delta); % Designing the decimation filter hi = hd; % Interpolation filter [Hk,Fk] = freqz(hk,1,1024,F0/2); [Hk2,F] = freqz(upsample(hk,2),1,1024,F0); [Hd,F] = freqz(hd,1,1024,F0); figure(1),plot(F,20*log10(abs(Hd))), ylabel('Gain [dB]'),xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'), grid on,axis([0,5000,-100,5]), title('Decimation and Interpolation Filters'), figure(2),plot(Fk,20*log10(abs(Hk))), ylabel('Gain [dB]'),xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'), grid on,axis([0,2500,-100,5]), title('Kernel Filter'); Hi = Hd; H = (Hd.*Hk2).*Hi; % The overall filter frequency response figure(3),plot(F,20*log10(abs(H))), ylabel('Gain [dB]'),xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'), grid on,axis([0,5000,-130,5]), title('Overall Multirate Filter'); g(1)=axes('Position',[0.40 0.70 0.40 0.1]); plot(F(1:180),(abs(H(1:180)))), axis([0,800,0.99,1.01]); [Hd_al,F]=freqz(hd,1,2048,F0,'whole'); Hd_a=Hd_al(1025:2048); Alias=(Hd_a.*Hk2).*Hi; % Aliasing characteristic figure(4),plot(F(1:1024),20*log10(abs(Alias)),'--'), ylabel('Gain [dB]'),xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'), grid on title('Aliasing Characteristic');
Exercise 9.2
Compose the multirate highpass filter consisting of a cascade
of a factor-of-2 decimator, kernel filter and factor-of-2 interpolator.
The specifications for the overall filter are the following:
- Sampling frequency: F0 = 10000 Hz
- Passband edge frequency Fp = 4200 Hz
- Stopband edge frequency Fs = 4000 Hz
- Minimal attenuation in the stopband as = 60 dB
- Peak passband ripple δp = 0.01.
- Decimation and interpolation filters are identical halfband
filters.
Compute and plot:
- Magnitude responses of decimation and interpolation filters
- Magnitude response of the kernel filter
- Magnitude response of the overall multirate filter
- Aliasing characteristic of the overall filter.
Used functions firgr (DSP System Toolbox), freqz (Signal Processing Toolbox)
close all, clear all F0 = 10000; % Sampling frequency [Hz] Fp = 4200; % Passband edge frequency [Hz] Fs = 4000; % Stopband edge frequency [Hz] delta = 0.001; % Peak stopband ripple % In the first step, we design lowpass decimation/interpolation filters, % and in the second step we convert lowpass decimation/interpolation % filters into highpass filters. In the third step, we design the lowpass % kernel filter, and compose the overall multirate highpass filter. % FIRST STEP % Computing the speciffications of the lowpass decimation/interpolation % filters Fp = F0/2-Fp; % Passband edge frequency [Hz] Fs = F0/2-Fs; % Stopband edge frequency [Hz] hd = firhalfband('minorder',(2*Fs + Fp)/(3*F0/2),delta); % Designing the decimation filter % SECOND STEP % Converting the lowpass filter from the first step into highpass filter n = 0:length(hd)-1; hd = hd.*(-1).^n; % Highpass decimation filter hi = hd; % Highpass interpolation filter [Hd,F] = freqz(hd,1,1024,F0); figure(1),plot(F,20*log10(abs(Hd))), ylabel('Gain [dB]'),xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'), axis([0,5000,-100,5]),grid on, title('Decimation and Interpolation Filters'); % THIRD STEP Nord_k = 82; % Setting the kernel filter order hk = firgr(Nord_k,[0,2*Fp/(F0/2),2*Fs/(F0/2),1],[1,1,0,0]); % Designing the kernel filter [Hk,Fk] = freqz(hk,1,1024,F0/2); [Hk2,F] = freqz(upsample(hk,2),1,1024,F0); figure(2),plot(Fk,20*log10(abs(Hk))), ylabel('Gain [dB]'),xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'), axis([0,2500,-100,5]), grid on, title('Kernel Filter'); Hi = Hd; H = (Hd.*Hk2).*Hi; % The overall filter frequency response figure(3),plot(F,20*log10(abs(H))), ylabel('Gain [dB]'),xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'), axis([0,5000,-130,5]),grid on; title('Overall Multirate Filter'); g(1)=axes('Position',[0.25 0.70 0.40 0.1]); plot(F(840:1024),(abs(H(840:1024)))),axis([4200,5000,0.99,1.01]); n=1:length(hd); [Hd_al,F]=freqz(hd,1,2048,F0,'whole'); Hd_a=Hd_al(1025:2048); Alias=(Hd_a.*Hk2).*Hi; % Aliasing characteristic figure(4),plot(F(1:1024),20*log10(abs(Alias)),'--'), ylabel('Gain [dB]'),xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'), grid on, title('Aliasing Characteristic');